Q1.Definitions
Field- are the smallest units of information you can access. Fields make records and records make up a databases
Record- Records are composed of fields, each of which contains one item of information. A set of records constitutes a file. For example, a personnel file might contain records that have three fields: a name field, an address field, and a phone number field.
File- is a collection of records. For example, a telephone book is analogous to a file. It contains a list of records, each of which consists of three fields: name, address, and telephone number.
Query-A request for information from a database. There are three general methods for posing queries: Choosing parameters from a menu: In this method, the database system presents a list of parameters from which you can choose. This is perhaps the easiest way to pose a query because the menus guide you, but it is also the least flexible. Query by example (QBE): In this method, the system presents a blank record and lets you specify the fields and values that define the query. Query language: Many database systems require you to make requests for information in the form of a stylized query that must be written in a special query language. This is the most complex method because it forces you to learn a specialized language, but it is also the most powerful.
Database-A collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can quickly select desired pieces of data. You can think of a database as an electronic filing system
Report-A formatted and organized presentation of data. Most database management systems include a report writer that enables you to design and generate reports DBMS-A collection of programs that enables you to store, modify, and extract information from a database. There are many different types of DBMSs, ranging from small systems that run on personal computers to huge systems that run on mainframes.
Data Dictionary-In database management systems, a file that defines the basic organization of a database. A data dictionary contains a list of all files in the database, the number of records in each file, and the names and types of each field. Most database management systems keep the data dictionary hidden from users to prevent them from accidentally destroying its contents. Data dictionaries do not contain any actual data from the database, only bookkeeping information for managing it. Without a data dictionary, however, a database management system cannot access data from the database.
Data Type-classification of a particular type of information.
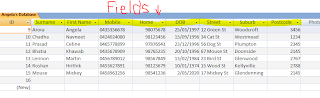
Q2.Table Showing Files and Records
As depicted from the above table of songs. This is an example of what records, fields and files.
Q3.Common Used Databases
There are many commonly used databases that are around us everyday such as:
- Library
- Phones
- Contacts
- Spreadsheets
- Information Records